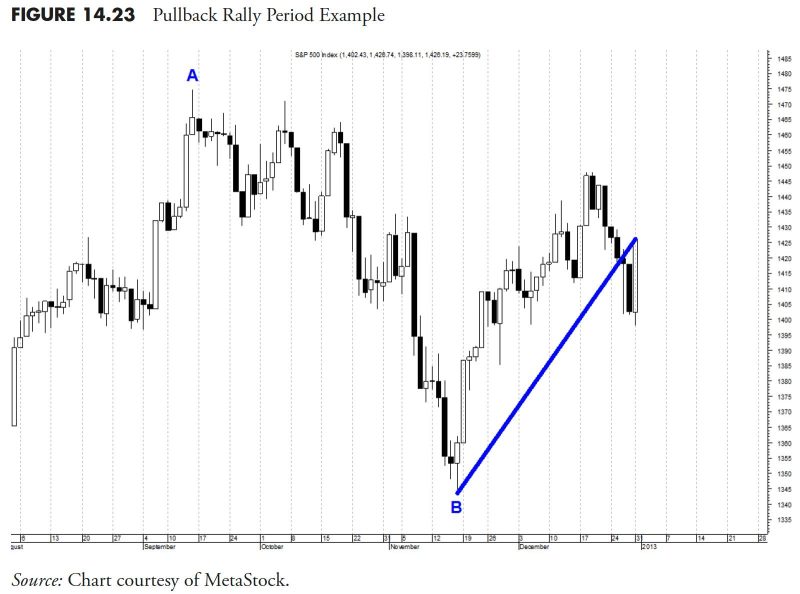
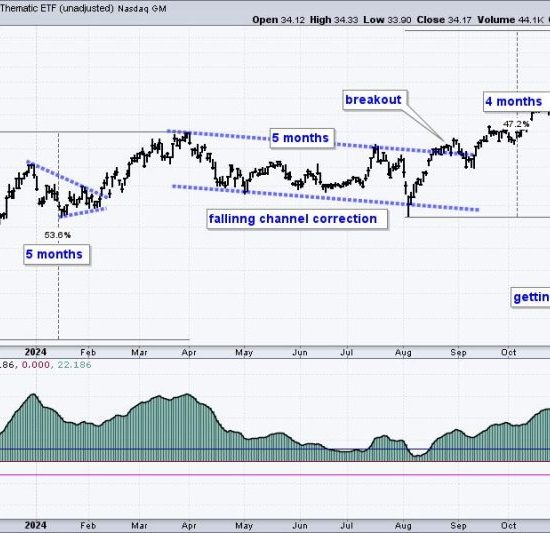
Section 1: Security Selection under a Rules-Based Money Management System
Security selection forms a significant part of a rules-based money management strategy. By adhering to an objectively defined set of rules, investors can streamline their investment decisions and mitigate potential risks. The rules-based approach can involve a number of strategies, such as utilizing fundamental or technical analysis, dividend yield, price volatility, or other trade-focused factors.
Depending on their financial goals, risk tolerance, time frame, and capital, investors can select from a plethora of security types. They can include equities, fixed-income securities, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), mutual funds, options, futures, commodities, or currencies. Each of these security types cater to different investment objectives and risk profiles, offering a crucial choice in rules-based money management.
Section 2: Deploying Rules for Security Selection
Investors need to craft their rules carefully to ensure optimal security selection. These rules should be in alignment with their investment goals, risk tolerance, and market understanding. By considering all these points, they can create a systematic approach to buying and selling their investments.
The rules for security selection can vary based on the investor’s strategy. For instance, a value-oriented investor might focus on stocks with low P/E ratios or high dividend yields. A growth investor, on the other hand, could prioritize companies with high earnings growth. Similarly, an income-focused investor might concentrate on bonds with high-quality credit ratings.
Furthermore, investors might also use technical analysis as a guiding principle. This involves analyzing price trends and patterns to predict future movements. Those who follow this approach could establish rules such as buying securities following a bullish trend or selling those exhibiting a bearish trend.
Section 3: Essential Guidelines in Rules-Based Money Management
Just as critical as security selection is the need to follow clear-cut guidelines in executing a rules-based money management system.
1. Consistency: Adherence to the chosen strategy and its embedded rules is crucial. Investors should avoid deviating from the rules based on emotional impulses or short-term market fluctuations.
2. Reviews and Adjustments: Regular reviews of the rules-based strategy are encouraged to assess its efficiency and make necessary adjustments. Over time, changes in market conditions, investment objectives or risk tolerance may require revising the set rules.
3. Diversification: Rules should promote adequate diversification across different securities or asset classes to manage risk more effectively.
4. Risk Management: The rules should outline clear risk management aspects, such as setting stop-loss orders or appropriate position sizing.
5. Exit Strategy: Clear rules regarding when to sell a security are as important as knowing when to buy. These can be based on achieving the target return, adverse changes in fundamentals, or technical signals indicating a potential price drop.
Incorporating these guidelines into the rules-based money management strategy can ensure more efficient security selection and improved overall portfolio performance.
Section 4: The Importance of Discipline and Patience
Even the best-formulated rules and guidelines are ineffective without discipline and patience. Adhering strictly to the established rules can keep emotions at bay and prevent ill-timed investment decisions. Meanwhile, having patience allows the investment strategy time to bear fruit, especially in scenarios where long-term returns are the goal.
Ultimately, a rules-based money management system offers a structured and objective framework through which investors can make informed security selection decisions. While it’s not a foolproof method guaranteeing returns, it ensures a more disciplined and measured approach to investing. Whether a seasoned investor or a novice, following a well-defined set of rules and guidelines can profoundly contribute towards effective investment management.