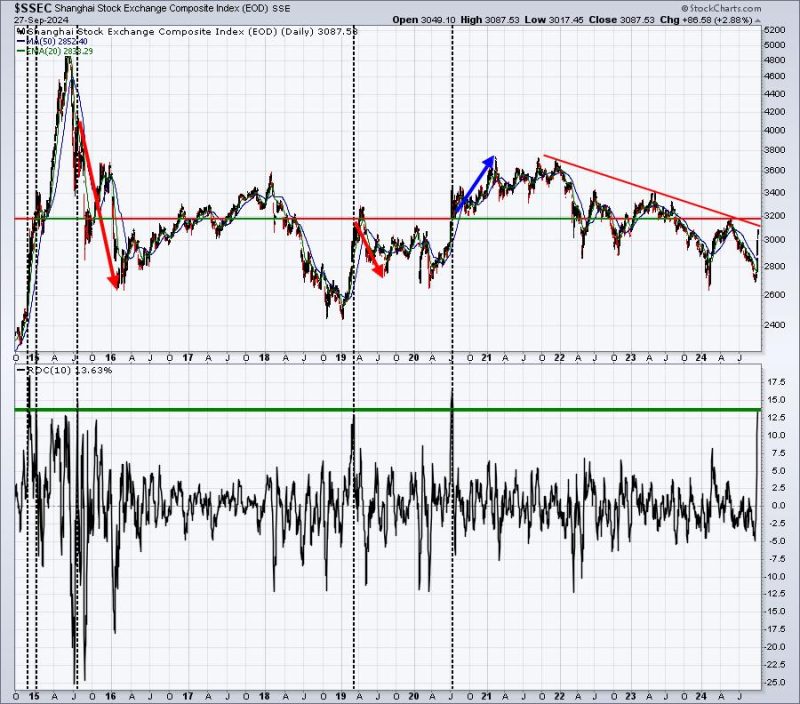
Last week, China’s financial market displayed remarkable strength that caught the eyes of investors and market observers worldwide. The Middle Kingdom has once again become a beacon of sturdy growth, amplified by a combination of factors that include policy support, economic recovery measures and a steady control of the Covid-19 situation. The question, however, now that has gripped market watchers is: can this strength shown by China in the recent past be sustained?
The key factors underlining China’s strength are manifold. First, stringent measures for virus control have enabled the Chinese economy to bounce back more swiftly than other major economies. Secondly, China’s central government introduced several major policy initiatives that boost domestic demand, facilitate deficit spending, and promote infrastructure development. Also not to forget the adoption of digitization and technology that accelerated despite the pandemic and powered economic growth.
However, the sustainability of this strength on a more long-term horizon is dependent upon an array of factors, namely, the global economic outlook, policy support, interest rates, technology development, geopolitical considerations, and the course of the pandemic among others.
China’s pandemic recovery model has been rooted in fiscal stimulation. The government deployed a massive fiscal stimulus package to drive domestic consumption and increase infrastructure spending. The implementation of these measures helped to pump trillions of yuan into the country’s economy thus stabilizing growth. However, a prolonged reliance on such measures will likely increase the risk of fiscal deficit, and may add pressures on the monetary policy, to balance the fiscal measure.
On the global front, uncertainty persists due the slowly recovering demand in the international markets, affecting its export-oriented economic sectors. If the global markets exhibit a robust recovery, it would reinforce China’s export strength. A sluggish recovery, however, could slow down the export-driven growth momentum, thereby impacting the sustainability of China’s economic strength.
The impact of geopolitical considerations also cannot be undermined. Tensions between China and countries like the U.S. and India may influence investor sentiment and hamper international trade and investment inflows. Therefore, keeping geopolitical tensions at bay is critical for the sustenance of China’s economic strength.
Interest rates and monetary policies are another influential factor. China adopted an accommodative monetary policy stance to cushion against the virus shock, which included measures like rate cuts and liquidity injection. While this has helped boost the economy in the short-run, the roll-back of these measures too soon could instigate financial market turbulence, thereby affecting the sustainability of the economy recovery.
In terms of technology capability, China is making strides in this sector, as evidenced by the strong performance of tech giants like Alibaba and Tencent. However, dealing with ever evolving global tech competition and navigating through regulation of its home-grown technology companies will be decisive in asserting China’s overall economic might.
Lastly, the course of the Covid-19 pandemic and China’s capability in controlling new outbreaks will determine the sustainability of its economic strength. Although China successfully contained the virus and was the first to rebound, any fresh resurgence of the virus cases could pose serious challenges.
While the signs of strength shown by China are promising, the future will depend on a complex interplay of domestic and global dynamics. To sustain this momentum, China’s policy makers will need to be adaptive and responsive to these challenges while treading on a path of balanced growth. The world, undoubtedly, will have its eyes affixed on China’s next moves.